Introduction
The clinical research world is undergoing a significant digital transformation. As studies become more patient-centric and data-driven, technology plays a growing role in streamlining processes and improving outcomes. One of the major shifts we’re seeing is the adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) strategies in clinical trials.
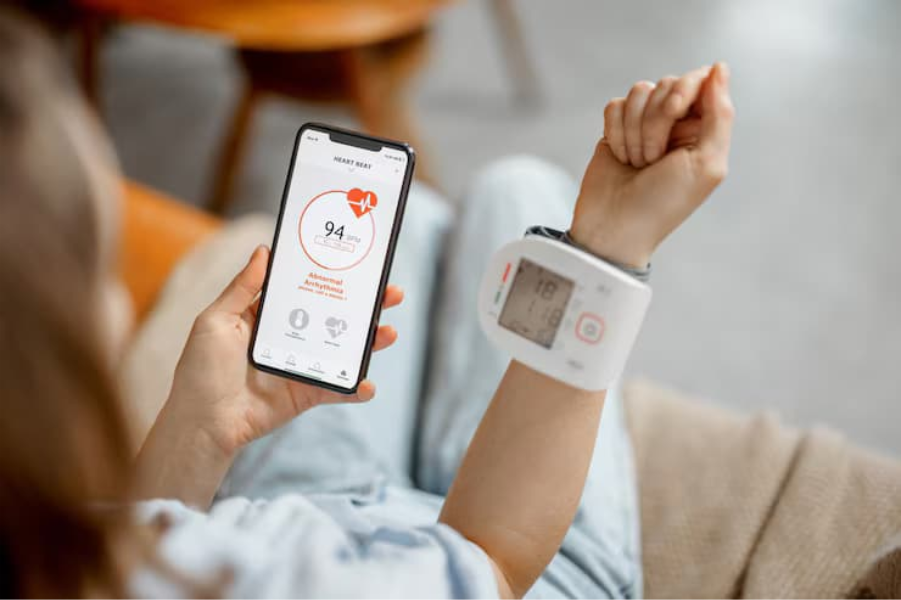
BYOD allows study participants to use their own smartphones or wearable devices to record health data, complete electronic diaries, or communicate with research teams. It’s an approach that offers convenience, scalability, and efficiency for both participants and trial sponsors. But like any innovation, it comes with its own set of considerations.
In this blog, we’ll explore what BYOD means for clinical research, how it can benefit your study, and what challenges to watch for. Whether you’re designing a new trial or optimizing an existing one, understanding BYOD can help you make informed decisions.
What Is BYOD in Clinical Trials?
BYOD stands for “Bring Your Own Device.” In clinical trials, it refers to the use of participants’ personal smartphones, tablets, or wearables for data collection and communication during a study. Instead of providing standardized devices to every participant, researchers allow them to use their own devices, often through a secure app or web portal.
This model contrasts with traditional clinical trial approaches, where sponsors supply specific equipment. While provisioning devices offers greater control, BYOD brings several advantages, especially as mobile technology becomes more powerful and widespread.
The BYOD approach is gaining popularity in studies involving electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO), remote monitoring, virtual visits, and digital biomarkers. It supports decentralized and hybrid trial models that reduce site visits and give patients more flexibility in how they participate.
Benefits of BYOD Strategies in Clinical Studies
1. Improved Patient Compliance
One of the most significant advantages of BYOD is improved patient compliance. Participants are more likely to engage with a study when they can use a device they already know. Familiarity leads to better adherence to study protocols, such as completing daily questionnaires, logging symptoms, or taking medications on schedule.
Instead of having to learn how to use a new device or carry an extra one, participants can simply install an app on their phone. This reduces the friction that often leads to dropouts or incomplete data collection.
2. Greater User Engagement
When patients use their own devices, they tend to interact more frequently with study tools. Notifications, reminders, and check-ins become a seamless part of their routine. Many people already use their phones to track health metrics like steps, sleep, and heart rate, so extending that behavior into clinical studies feels natural.
Engaged participants provide more accurate and timely data. They’re also more likely to stay enrolled through the duration of the study, which improves retention rates and data integrity.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Supplying and managing devices for every participant can be costly. There’s the expense of purchasing hardware, configuring software, shipping, support, and potentially retrieving or replacing lost devices. These costs can quickly add up, especially in large or global studies.
BYOD significantly reduces these costs. Sponsors don’t need to buy or ship devices, which lowers the initial investment and cuts down on logistical complexities. This makes studies more scalable and financially sustainable, especially when targeting diverse or hard-to-reach populations.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
With BYOD, scaling up a study is much easier. There’s no need to wait for device inventory or manage shipping logistics. Participants from different countries or regions can be onboarded quickly, as long as they meet device compatibility requirements.
This flexibility is especially valuable for studies with rolling enrollment or adaptive designs. It also supports decentralized trial models where participants may never need to visit a physical site.
5. Real-World Data Collection
Using personal devices allows data to be collected in real-world settings. Participants are more likely to behave naturally when they’re not being monitored in a clinical environment. This results in data that better reflects how patients actually experience symptoms and treatments in daily life.
Real-world data enhances the generalizability of trial findings and can lead to deeper insights. It also supports the use of digital biomarkers—objective, quantifiable physiological data collected through connected technologies—for more accurate monitoring and analysis.
Challenges in Implementing BYOD Approaches
While BYOD brings many benefits, it also presents challenges that researchers must carefully address. Let’s explore some of the most common concerns.
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Security is a top priority in clinical research. Personal health information must be protected at all times. When participants use their own devices, there are more variables to control. Devices may have different security settings, outdated software, or vulnerabilities that could expose sensitive data.
To address this, study apps must be designed with strong encryption, user authentication, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. Clear data policies and participant education are also important to ensure security on both ends.
2. Device Compatibility and Standardization
Not all smartphones are created equal. Differences in operating systems (iOS vs Android), screen sizes, and processing power can affect how apps run and how data is collected. Ensuring a consistent experience across multiple devices is a technical challenge.
Clinical teams must test their software across a wide range of devices and OS versions. Setting minimum device requirements and providing a fallback option—like offering provisioned devices to those whose phones are incompatible—can help reduce risk.
3. Technical Support and Patient Training
Even though participants are using their own devices, they may still need help with setup, troubleshooting, or navigating the app. A lack of support can lead to frustration, missed data, or participant dropout.
It’s important to offer accessible, user-friendly onboarding materials, such as video tutorials or in-app guides. A responsive help desk can also ensure quick resolution of any technical issues.
Platforms like Delve Health offer end-to-end support, including 24/7 participant assistance, which ensures a smoother experience for users and better data for sponsors.
4. Regulatory and Validation Requirements
Regulatory bodies expect that clinical data is collected in a consistent and validated manner. Using a range of personal devices can complicate validation. Researchers must demonstrate that data collected through BYOD is equivalent in quality and reliability to that from provisioned devices.
This requires proper documentation, quality control measures, and collaboration with software partners who understand compliance requirements. Working with an experienced vendor like Delve Health, who has built regulatory-ready BYOD solutions, can simplify this process.
How to Design an Effective BYOD Strategy
Implementing BYOD in a clinical trial requires thoughtful planning and collaboration. Here are the key elements to consider:
Assess Your Target Population
Start by understanding the tech habits of your intended participants. Are they comfortable using smartphones? What platforms do they typically use? In some studies, it may be more practical to use provisioned devices, especially with older populations or those in areas with limited internet access.
Choose the Right Technology Platform
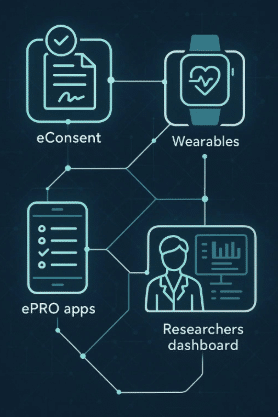
Look for a digital trial platform that is device-agnostic, secure, and built for clinical compliance. Features like ePRO integration, remote monitoring, and wearable data syncing should be supported across both iOS and Android devices.
Delve Health, for instance, offers a unified platform that supports BYOD, wearable integration, and decentralized trials—all while meeting global regulatory standards.
Ensure Data Quality and Standardization
Use robust software that can normalize data across devices and detect inconsistencies in real time. Include validation checks, audit trails, and the ability to flag potential errors. Automated prompts can remind participants to complete assessments or recheck readings.
Provide Training and Support
Offer simple guides, onboarding calls, and technical help to get participants set up. Make sure your support team is trained to handle questions related to different devices, operating systems, and app features.
Monitor and Adapt
Even after launch, continue to monitor device usage patterns and feedback. Make updates to improve usability, address technical issues, or expand compatibility. This iterative approach helps you continuously improve the experience for participants and researchers alike.
The Future of BYOD in Clinical Trials
The future of clinical research is clearly moving toward decentralization, flexibility, and patient empowerment. BYOD is central to this evolution.
As mobile technology advances and wearable devices become more sophisticated, the ability to gather real-time health data from patients’ own environments will only increase. Digital biomarkers, AI-driven analytics, and integrated remote monitoring will all benefit from BYOD infrastructure.
Regulatory bodies are also becoming more supportive of BYOD, especially as they see consistent evidence of its effectiveness. The key is to maintain rigorous data standards while expanding access to more diverse patient populations.
Platforms like Delve Health are helping lead the way, offering turnkey solutions that combine BYOD, wearable integration, and decentralized trial design. These tools are making it easier for research teams to innovate while ensuring compliance and reliability.
Conclusion
Implementing a BYOD strategy in your clinical trial can unlock many advantages—better patient compliance, lower costs, faster enrollment, and richer data. But it also requires careful planning around security, compatibility, and support.
The key to success lies in partnering with the right technology provider. Delve Health offers a flexible, secure, and scalable platform designed specifically for modern clinical research. Whether you’re running a fully virtual study or adding digital tools to a traditional trial, their expertise can help you implement BYOD the right way.
If you’re ready to explore how BYOD could fit into your clinical research, consider reaching out to Delve Health to learn how their solutions can support your goals.
FAQs
1. What are the main advantages of BYOD in clinical research?
BYOD improves patient compliance, lowers study costs, and speeds up enrollment by allowing participants to use their own devices. It also enables real-world data collection and supports decentralized trial models.
2. How can data security be ensured in a BYOD model?
Security is maintained through encrypted apps, strict data policies, and user authentication. Partnering with compliant platforms ensures adherence to HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory standards.
3. Is BYOD more cost-effective than providing study devices?
Yes, BYOD eliminates the need to buy, ship, and maintain study-specific devices. This reduces costs significantly, especially in large-scale or multi-region trials.
4. What types of trials are best suited for BYOD strategies?
BYOD works well for trials using ePROs, remote monitoring, or digital biomarkers. It’s ideal for decentralized or hybrid trials and populations comfortable with smartphones and wearables.
5. How can Delve Health help implement BYOD in my clinical study?
Delve Health provides a validated, secure platform for BYOD studies, including ePRO tools, wearable integration, and 24/7 support. They guide you from planning to execution for a smooth rollout.