The Importance of Doing Something Different with Gathering Patient Outcomes
Gathering accurate patient outcomes is more crucial than ever. This article explores the necessity of adopting new methods, particularly through wearables and digital biomarkers, to enhance the realism and utility of clinical data.
Introduction
The landscape of healthcare is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological advancements that promise to revolutionize patient care and clinical research. The global market for wearable devices is expanding rapidly, with over 500 million wearable devices estimated to be in use worldwide by 2024. This represents a significant increase from just a few years ago, highlighting the growing adoption and reliance on this technology. Traditionally, patient outcomes have been gathered through subjective means, such as self-reported diaries and infrequent clinical visits. While these methods have their place, they often fall short of capturing the dynamic and nuanced nature of patients’ real-world experiences. Enter wearables and digital biomarkers—innovations that offer a more accurate, continuous, and holistic view of patient health. This shift towards real-time data collection not only enhances the quality of clinical research but also empowers individuals to take a more active role in managing their health.
Why Traditional Methods of Gathering Patient Outcomes Are Inadequate
Traditional methods of gathering patient outcomes, such as periodic check-ins and patient self-reports, have long been the backbone of clinical research. However, these methods come with significant limitations. The episodic nature of clinic visits means that only a fraction of a patient’s experience is captured, often missing critical variations in their condition. Self-reports, while valuable, are subject to recall bias and inaccuracies. Consequently, the data collected may not fully represent the patient’s true health status, leading to suboptimal treatment decisions and research conclusions.
The Emergence of Wearables in Healthcare
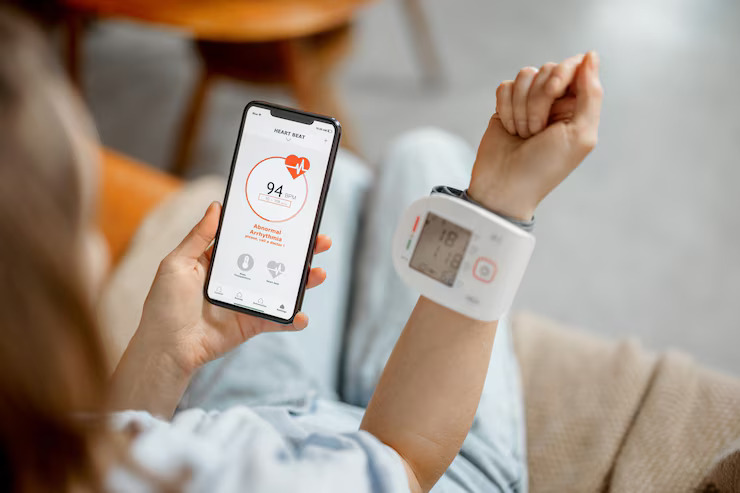
Wearable technology has emerged as a game-changer in healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to gather continuous and objective data on various health parameters. Devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical wearables can monitor a range of metrics, including heart rate, physical activity, sleep patterns, and more. These devices provide a wealth of real-time data that is both granular and comprehensive, painting a detailed picture of a patient’s health over time.
Advantages of Wearables in Gathering Patient Outcomes
Wearables offer several key advantages over traditional methods. Firstly, they enable continuous monitoring, capturing data around the clock and providing insights into daily fluctuations and trends. This continuous stream of data is particularly valuable in understanding chronic conditions and the impact of lifestyle factors on health. Secondly, wearables eliminate the need for patient self-reporting, reducing the risk of recall bias and increasing the accuracy of the data collected. Finally, the real-time feedback provided by wearables can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health and prompt timely interventions by healthcare providers.
Digital Biomarkers: A New Frontier in Clinical Research
Digital biomarkers are objective, quantifiable measures obtained through digital devices that can be used to monitor health and disease. They represent a new frontier in clinical research, offering more precise and individualized data compared to traditional biomarkers. Digital biomarkers can be derived from a variety of sources, including physiological signals (e.g., heart rate variability), behavioral patterns (e.g., activity levels), and even environmental factors (e.g., exposure to pollutants).
The Role of Digital Biomarkers in Enhancing Clinical Research
The integration of digital biomarkers into clinical research holds the potential to transform the field in several ways. Firstly, digital biomarkers can improve the sensitivity and specificity of health assessments, enabling earlier detection of disease and more accurate monitoring of disease progression. Secondly, they can facilitate personalized medicine by providing insights into how different individuals respond to treatments, allowing for more tailored and effective interventions. Thirdly, digital biomarkers can enhance the efficiency of clinical trials by providing real-time data, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits, and enabling remote monitoring of participants.
How Wearables and Digital Biomarkers Improve Data Realism
One of the most significant benefits of using wearables and digital biomarkers is the increased realism of the data collected. Traditional clinical settings often fail to capture the full spectrum of a patient’s daily experiences, leading to a gap between clinical data and real-world outcomes. Wearables, by contrast, provide continuous, context-rich data that reflects the patient’s actual living conditions. This real-world data is invaluable for understanding how treatments perform outside of controlled clinical environments and can lead to more effective and applicable healthcare solutions.
Empowering Patients Through Wearable Technology
Wearables not only benefit clinical research but also empower patients to take control of their health. By providing real-time feedback and personalized insights, wearables can motivate individuals to adopt healthier behaviors and make informed decisions about their care. For instance, a patient with a chronic condition can use wearable data to identify triggers and patterns, leading to better self-management and improved outcomes. Additionally, the data collected by wearables can facilitate more informed and productive conversations between patients and healthcare providers, leading to more collaborative and effective care plans.
Case Studies: Successful Integration of Wearables in Clinical Research
Numerous case studies highlight the successful integration of wearables in clinical research. For example, the Apple Watch has been approved by the FDA for its atrial fibrillation (AFib) detection capabilities. This wearable device not only monitors heart rate but also identifies irregular heart rhythms, which are critical indicators of AFib. In clinical studies, the Apple Watch’s ability to accurately detect AFib has been validated, making it a valuable tool for both patients and healthcare providers. The FDA’s approval of the Apple Watch for AFib detection underscores the potential of wearables to serve as reliable endpoints in clinical research, enhancing the quality and relevance of the data collected. This kind of integration showcases how wearable technology can be brought into hospitals and healthcare systems, improving clinical outcomes and streamlining patient monitoring.
Challenges and Considerations in Using Wearables for Clinical Research
Despite the many advantages of wearables, there are also challenges and considerations to address. One key issue is data privacy and security, as the continuous monitoring and collection of personal health data raise concerns about confidentiality and data protection. Ensuring that data is stored and transmitted securely is paramount. Additionally, the accuracy and reliability of wearable devices can vary, necessitating rigorous validation and standardization to ensure that the data collected is of high quality. Finally, there is a need for greater integration and interoperability between different wearable devices and healthcare systems to maximize the utility of the data collected.
The Future of Wearables and Digital Biomarkers in Healthcare
Looking ahead, the future of wearables and digital biomarkers in healthcare is promising. Advances in sensor technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are poised to further enhance the capabilities of wearable devices, enabling even more precise and comprehensive health monitoring. Additionally, as more individuals adopt wearables, the potential for large-scale population health studies increases, offering new opportunities to understand health and disease at a macro level. Ultimately, the continued evolution of wearables and digital biomarkers will play a crucial role in advancing personalized medicine and improving patient outcomes.
Wearables in Chronic Disease Management
Wearables are particularly valuable in the management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and respiratory conditions. Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of exacerbations, enabling timely interventions that can prevent complications and hospitalizations. For example, a wearable glucose monitor can provide real-time feedback to a diabetic patient, helping them to better manage their blood sugar levels. Similarly, a wearable blood pressure monitor can alert a hypertensive patient to spikes in their blood pressure, prompting them to take corrective action. By providing continuous, actionable data, wearables can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions.
The Role of Wearables in Preventive Health
In addition to managing chronic diseases, wearables also have a crucial role to play in preventive health. By monitoring key health metrics and providing personalized insights, wearables can help individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles and reduce their risk of developing chronic conditions. For instance, a wearable fitness tracker can encourage users to increase their physical activity, while a wearable sleep tracker can help users to improve their sleep hygiene. By promoting healthy behaviors and providing early warnings of potential health issues, wearables can contribute to better overall health and well-being.
Integrating Wearables into Clinical Practice
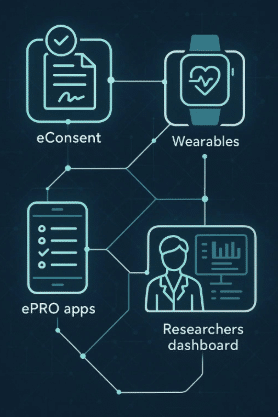
To fully realize the potential of wearables in healthcare, it is essential to integrate them into clinical practice. This involves not only the adoption of wearable technology by healthcare providers but also the development of systems and protocols for utilizing wearable data in patient care. Healthcare providers need to be trained in the use of wearables and digital biomarkers, and electronic health records (EHRs) must be adapted to incorporate data from wearable devices. By integrating wearables into routine clinical practice, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care and improve patient outcomes.
Patient Engagement and Adherence
One of the significant benefits of wearables is their ability to engage patients in their health and encourage adherence to treatment plans. Wearable devices can provide reminders to take medications, attend appointments, and perform prescribed exercises, helping patients to stay on track with their treatment plans. Additionally, the real-time feedback provided by wearables can motivate patients to make positive changes and adhere to healthy behaviors. By fostering greater patient engagement and adherence, wearables can contribute to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
The Economic Impact of Wearables in Healthcare
The economic impact of wearables in healthcare is another important consideration. By enabling early detection and intervention, wearables can help to reduce healthcare costs associated with chronic diseases and hospitalizations. Additionally, the use of wearables in clinical research can streamline the research process, reducing the time and cost of conducting studies. As wearable technology continues to evolve and become more widespread, the potential for cost savings in healthcare is significant.
The Ethical Implications of Wearable Technology
While the benefits of wearables are clear, it is also important to consider the ethical implications of this technology. Issues such as data privacy, consent, and equity must be addressed to ensure that the use of wearables is ethical and equitable. Patients must be fully informed about how their data will be used and have the ability to opt out if they choose. Additionally, there is a need to ensure that the benefits of wearable technology are accessible to all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status or access to healthcare. This calls for policies and frameworks that promote inclusivity and safeguard patient rights while harnessing the full potential of wearable technologies.
The Integration of Wearables into Hospitals and Healthcare Systems
The integration of wearable technology into hospitals and healthcare systems is a critical next step in the evolution of healthcare. By leveraging the continuous and comprehensive data provided by wearables, healthcare providers can improve patient monitoring, enhance clinical decision-making, and streamline hospital operations. For instance, continuous monitoring of patients in a hospital setting can help in early detection of potential complications, leading to prompt interventions and improved patient outcomes. Additionally, the data collected from wearables can be seamlessly integrated into electronic health records (EHRs), providing a more holistic view of patient health and facilitating more personalized care.
Moreover, the integration of wearables into healthcare systems can support population health management by identifying trends and patterns across different patient populations. This can inform public health strategies, resource allocation, and preventive care initiatives. As hospitals and healthcare systems increasingly adopt wearable technology, they will be better equipped to meet the challenges of modern healthcare and deliver higher quality care to patients.
Conclusion
The shift towards using wearables and digital biomarkers to gather patient outcomes represents a significant advancement in healthcare and clinical research. These technologies offer more accurate, continuous, and holistic data, bridging the gap between clinical settings and real-world experiences. By integrating wearables into clinical practice and healthcare systems, we can enhance patient care, improve clinical research, and ultimately, drive better health outcomes. The future of healthcare lies in embracing these innovations and ensuring that they are accessible, ethical, and effectively utilized for the benefit of all.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do wearables improve the accuracy of patient outcomes? Wearables provide continuous, real-time data that reflects a patient’s daily life and experiences, offering a more comprehensive and accurate picture of their health compared to traditional methods.
What are digital biomarkers? Digital biomarkers are objective, quantifiable measures obtained through digital devices used to monitor health and disease, providing more precise and individualized data compared to traditional biomarkers.
Why are wearables important in clinical research? Wearables enhance clinical research by providing continuous, real-time data, improving the sensitivity and specificity of health assessments, and enabling remote monitoring of participants.
How can wearables benefit patients with chronic conditions? Wearables allow for continuous monitoring of health metrics, enabling early detection of exacerbations and timely interventions, improving disease management and quality of life for patients with chronic conditions.
What are the challenges of using wearables in healthcare? Challenges include ensuring data privacy and security, validating the accuracy and reliability of wearable devices, and integrating wearable data into healthcare systems.
How do wearables support preventive health? Wearables monitor key health metrics and provide personalized insights, encouraging healthier behaviors and reducing the risk of developing chronic conditions.