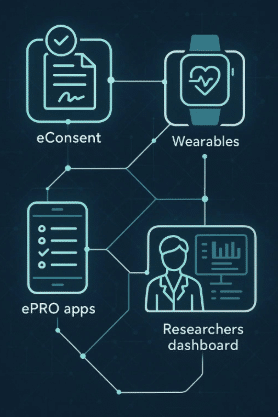
Wearable technology has transformed clinical trials, providing new ways to gather precise patient data in real time. Devices like smartwatches and biosensors are changing the way medical research is conducted.
The integration of wearables in clinical trials brings exciting possibilities:
- Continuous Data Collection: Real-time monitoring of patient metrics 24/7
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Reduced site visits and improved study adherence
- Data Accuracy: Elimination of manual recording errors
- Remote Monitoring: Ability to conduct decentralized trials effectively
However, using wearables in clinical trials is not as straightforward as giving devices to participants. A strong regulatory framework is necessary to ensure:
- Data validity and reliability
- Patient privacy protection
- Device accuracy and consistency
- Compliance with international standards
This article discusses the important regulatory factors that need to be considered for successfully using wearables in clinical trials. We will cover:
- Global regulatory landscapes and requirements
- Data management challenges and solutions
- Compliance requirements across different regions
- Ethical considerations
- Patient acceptance factors
Research organizations must understand these regulatory factors if they want to use wearable technology effectively while keeping their studies valid and their participants safe.
Regulatory Guidance for Wearables in Clinical Trials
The integration of wearable devices in clinical trials has sparked a complex regulatory landscape that demands careful navigation. Let’s dive into how different regulatory bodies approach these innovative technologies and what it means for your clinical trials.
Global Regulatory Landscape
FDA’s Approach
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has established specific guidelines for using digital health technologies in clinical investigations. Their framework includes:
- Digital Endpoints Validation: Requirements for demonstrating the reliability and accuracy of wearable-generated data
- Device Classification: Risk-based categorization determining the level of regulatory control
- Pre-Certification Program: Streamlined approval process for software-based medical technologies
The FDA’s Digital Health Innovation Action Plan provides a roadmap for evaluating real-world evidence from wearables, emphasizing:
- Verification of data accuracy
- Clinical validation protocols
- Cybersecurity requirements
- Patient privacy protection measures
EMA’s Regulatory Framework
The European Medicines Agency takes a distinct approach, focusing on:
- Data Quality Standards: Strict requirements for data integrity and reliability
- GDPR Compliance: Enhanced privacy protection measures for personal health data
- Technical Documentation: Detailed requirements for device specifications and validation
Regional Variations
Different regions present unique regulatory challenges:
Asia-Pacific
- Japan: Requires additional local validation studies
- China: Mandates local testing and certification
- South Korea: Emphasizes cybersecurity protocols
North America
- Canada: Harmonized with FDA guidelines but maintains independent review
- Mexico: Requires Spanish language documentation and local representation
Europe
- Individual member states may impose additional requirements
- Variations in data protection laws beyond GDPR
- Different interpretations of common guidelines
Impact on Multinational Trials
These regulatory differences create specific challenges:
- Protocol Design: Need for flexible study designs that accommodate regional requirements
- Data Collection: Implementation of multiple data standards
- Timeline Management: Variable approval processes affecting study initiation
- Cost Implications: Additional resources needed for regional compliance
Clinical trial sponsors must develop comprehensive regulatory strategies that address:
- Device certification requirements
- Data protection standards
- Local reporting obligations
- Safety monitoring protocols
- Risk management procedures
The key to successful implementation lies in early engagement with regulatory authorities and thorough understanding of regional requirements. This proactive approach helps identify potential roadblocks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
As we explore the potential of eClinical trials enhanced by wearables, such as the Apple Watch, it’s crucial to stay informed about these evolving regulations to fully leverage the benefits of these technologies in clinical research.

Future Directions for Regulation
The regulatory landscape for wearables in clinical trials is rapidly evolving. Industry experts predict significant changes in regulatory frameworks as these devices become increasingly prevalent in research settings, presenting opportunities in transforming clinical research in the US.
Key Anticipated Changes:
- Development of standardized validation protocols for digital endpoints
- Creation of unified data quality standards across regions
- Implementation of streamlined approval processes for wearable devices
- Establishment of clear guidelines for remote monitoring practices
- Integration of real-world evidence requirements
The FDA’s Digital Health Innovation Action Plan signals a shift toward modernizing regulatory approaches. This initiative aims to create a precertification program for digital health developers, potentially accelerating the approval process for wearable technologies.
Industry Collaboration Initiatives:
- Clinical Trials Transformation Initiative (CTTI) brings together stakeholders to develop best practices
- Digital Medicine Society (DiMe) works on establishing evaluation frameworks
- TransCelerate BioPharma focuses on creating standardized approaches for digital health technologies
- Digital Health Regulatory Pathways Project coordinates cross-border regulatory efforts
These collaborative efforts are essential for:
- Defining acceptable digital endpoints
- Creating standardized validation methods
- Establishing data quality benchmarks
- Developing security protocols
- Setting interoperability standards
The Patient Engagement Collaborative between FDA and European regulators demonstrates the growing emphasis on incorporating patient perspectives into regulatory decisions. This approach helps ensure wearable implementation addresses both scientific rigor and user needs.
Regional regulatory bodies are exploring “regulatory sandboxes” – controlled testing environments for innovative technologies. These programs allow companies to test new wearable solutions while maintaining patient safety standards.
The rise of decentralized clinical trials is pushing regulators to adapt their frameworks. New guidance focuses on:
- Remote consent processes
- Virtual monitoring procedures
- Data integrity verification methods
- Patient privacy protection measures
- Cross-border data sharing protocols
Data Management Challenges in Clinical Trials with Wearables
The integration of wearable devices in clinical trials brings unprecedented data management complexities. These sophisticated devices generate massive volumes of continuous data streams, creating unique challenges for research teams and data managers.
Ensuring Data Quality Throughout the Trial Process
Data quality is crucial for reliable clinical research outcomes. The use of wearable devices requires strong quality control measures at every stage:
Data Collection Phase
- Real-time data validation checks to identify anomalies
- Automated alerts for missing or inconsistent data points
- Regular device calibration and synchronization protocols
- Standardized procedures for handling connectivity issues
Data Processing Requirements
- Structured data cleaning protocols
- Automated error detection algorithms
- Data normalization across different device types
- Version control systems for data processing methods
The volume and speed of wearable data require advanced quality assurance measures:
Continuous Monitoring Systems
- Real-time data quality metrics
- Automated quality control checkpoints
- Regular system performance audits
Data Integrity Verification
- Hash functions to ensure data hasn’t been altered
- Audit trails for all data modifications
- Time-stamping mechanisms for data authenticity
Error Prevention Strategies
- Built-in data validation rules
- User authentication protocols
- Automated data backup systems
Clinical trial teams must establish clear data governance frameworks:
“Quality control measures should be embedded within every step of the data lifecycle, from collection through analysis, ensuring consistency and reliability in trial outcomes.”
Key Quality Control Components:
- Standardized data collection protocols
- Regular staff training programs
- Documentation of all quality control procedures
- Periodic quality assessments
- Clear escalation pathways for data issues
The implementation of these measures requires:
- Advanced data management platforms
- Skilled technical personnel
- Regular system updates
- Comprehensive documentation practices
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Redundant data storage systems
- Regular data reconciliation processes
- Contingency plans for device malfunctions
- Clear protocols for handling data discrepancies
Research teams must balance automated and manual quality control processes:
- Automated checks for large-scale data validation
- Manual review of flagged anomalies
- Regular quality control meetings
- Documentation of all quality-related decisions
These comprehensive quality control measures ensure:
Data accuracy and completeness
- Regulatory compliance
- Patient safety
- Scientific validity of trial results
The success of wearable integration in clinical trials depends on maintaining high data quality standards through systematic quality control processes and robust data management practices.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies for Efficient Data Handling
Cloud-based platforms are changing the way clinical trials manage data from wearable devices. These advanced systems offer features like real-time data syncing, automated quality checks, and secure sharing options for authorized stakeholders.
Key technological advantages include:
Automated Data Integration
- Direct streaming from wearable devices
- Standardized data formatting
- Real-time error detection
- Immediate data validation
Scalable Storage Solutions
- Elastic capacity adjustment
- Cost-effective data management
- Built-in redundancy
- Automatic backup systems
Modern cloud platforms come with advanced security features:
- End-to-end encryption
- Role-based access control
- Audit trail tracking
- Compliance with HIPAA and GDPR requirements
These platforms enable research teams to:
- Process large volumes of continuous data streams
- Apply machine learning algorithms for pattern recognition
- Generate automated alerts for data anomalies
- Create customized dashboards for different stakeholders
The integration of artificial intelligence enhances data analysis by:
- Identifying potential data quality issues
- Detecting patterns in participant behavior
- Flagging protocol deviations
- Streamlining data cleaning processes
Cloud-based systems also facilitate:
“Remote monitoring capabilities allow research teams to track study progress in real-time, enabling rapid response to any data collection issues or participant concerns.”
Advanced analytics tools within these platforms help:
- Visualize complex datasets
- Generate automated reports
- Track participant compliance
- Monitor device performance metrics
Research teams can leverage these technological capabilities to maintain data integrity while reducing manual processing time and minimizing human error in data handling procedures.
Compliance Requirements for Wearable Technology in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials using wearable devices must follow strict rules to protect participant data and ensure trial validity. Let’s explore the important compliance requirements that influence the use of wearables in clinical research.
Key Compliance Standards:
- 21 CFR Part 11 – Electronic records and signatures
- HIPAA – Healthcare data privacy in the US
- GDPR – Data protection in the EU
- ISO 14155 – Clinical investigation of medical devices
Electronic Records Compliance
Wearable devices generate large amounts of electronic data that need specific validation processes. According to 21 CFR Part 11, clinical trial sponsors must:
- Implement secure user authentication systems
- Maintain audit trails for all data modifications
- Conduct regular system validation checks
- Document backup procedures
- Follow electronic signature protocols
Addressing Compliance Across Regions
GDPR Requirements:
- Clear participant consent mechanisms, which can be streamlined through eConsent solutions
- Right to data access and deletion
- Data minimization principles
- Privacy impact assessments
- Appointment of data protection officers
HIPAA Considerations:
- Protected health information (PHI) encryption
- Access controls and authentication
- Security risk assessments
- Business associate agreements
- Breach notification protocols
Regional Compliance Strategies:
- Data Localization
- Protocol Harmonization
- Documentation Requirements
Data Localization
- Local data storage solutions
- Region-specific servers
- Geographical data segregation
Protocol Harmonization
- Unified data collection methods
- Standardized consent processes
- Compatible security measures
Documentation Requirements
- Multi-language participant materials
- Region-specific regulatory submissions
- Local ethics committee approvals
Practical Implementation Steps:
- Map applicable regulations for each trial location
- Develop comprehensive compliance matrices
- Implement robust data protection measures
- Create standardized operating procedures
- Train staff on regional requirements
Risk Mitigation Approaches:
- Regular compliance audits
- Real-time monitoring systems
- Automated compliance checks
- Documented validation processes
- Incident response protocols
Clinical trial sponsors can maintain global compliance while preserving data integrity by implementing these structured approaches. A well-designed compliance strategy enables seamless wearable integration while protecting participant rights across different jurisdictions.
The complexity of managing multi-regional trials requires careful attention to local regulatory nuances. Successful implementation depends on building flexible systems that can adapt to evolving compliance requirements while maintaining consistent data quality standards.
Ethical Considerations in Implementing Wearables
The integration of wearable devices in clinical trials brings unique ethical challenges that require careful consideration and strategic planning. Ethics committees face new complexities when evaluating study protocols involving these innovative technologies.
Balancing Innovation with Ethical Standards
Ethical review boards assess wearable technology implementation through several critical lenses:
Participant Autonomy
- Clear explanation of data collection methods
- Detailed information about device functionality
- Freedom to withdraw without consequences
- Options for temporary device removal
Privacy Protection Measures
- Data encryption standards
- Storage security protocols
- Access control mechanisms
- Third-party data sharing policies
Ethics committees examine how research teams address potential vulnerabilities:
Physical Considerations
- Skin irritation risks
- Device comfort levels
- Battery life management
- Emergency removal procedures
Psychological Impact
- Anxiety from continuous monitoring
- Stress from technical difficulties
- Social stigma concerns
- Impact on daily routines
The evaluation process includes rigorous assessment of:
“Research protocols must demonstrate robust safeguards for participant welfare while maintaining scientific validity”
Data Management Ethics
- Real-time monitoring boundaries
- Alert threshold determinations
- Incident response protocols
- Data deletion procedures
Ethics committees require specific documentation addressing:
Consent Process Clarity
- Language accessibility
- Technical term explanations
- Visual aids and demonstrations
- Participant rights documentation
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Technical support availability
- Backup data collection methods
- Device malfunction protocols
- Adverse event reporting systems
Cultural Sensitivity Considerations
- Religious observance accommodations
- Gender-specific concerns
- Cultural practice respect
- Community engagement strategies
Ethics committees evaluate the balance between scientific advancement and participant protection through:
Regular Protocol Reviews
- Safety monitoring reports
- Participant feedback analysis
- Device performance metrics
- Protocol adjustment needs
Stakeholder Communication
- Participant engagement methods
- Research team training
- Sponsor responsibilities
- Community outreach plans
The ethical framework must adapt to technological evolution while maintaining core principles of:
- Beneficence
- Non-maleficence
- Justice
- Respect for persons
Building Trust Through Transparency
Building participant trust in clinical trials using wearables requires a robust communication framework centered on transparency and continuous engagement. Here’s how research teams can create an environment of openness and trust:
Clear Communication Channels
- Dedicated support hotlines for technical assistance
- Regular check-ins through preferred communication methods
- Real-time updates on study progress via secure participant portals
- Multilingual support options for diverse participant populations
Data Usage Transparency
- Detailed explanations of how wearable data is collected and analyzed
- Regular updates on data security measures
- Clear documentation of third-party access protocols
- Visual representations of data flow throughout the study
Participant Empowerment Strategies
- Access to personal data collected through wearables
- Options to control data sharing preferences
- Rights to withdraw consent at any stage
- Ability to flag concerns or anomalies in data collection
Privacy Protection Measures
- Implementation of data anonymization techniques
- Secure encryption protocols for data transmission
- Regular security audits and updates
- Clear incident response procedures
Research teams must prioritize creating detailed consent forms that explain:
“Your wearable device collects [specific data points] every [time interval]. This information helps us understand [specific research objectives] while maintaining your privacy through [security measures].”
Ethical review boards play a crucial role in validating these transparency measures by:
- Reviewing communication materials for clarity and completeness
- Assessing the adequacy of privacy protection mechanisms
- Evaluating participant feedback systems
- Monitoring ongoing compliance with transparency commitments
Successful implementation of these strategies creates a foundation of trust that supports participant retention and data quality throughout the clinical trial process.
Patient Acceptance and User Experience
The success of wearable devices in clinical trials depends on whether patients accept and engage with them. By understanding the factors that influence adoption rates, researchers can design studies that are more effective and achieve higher compliance rates.
Factors Influencing Patient Acceptance Beyond Device Functionality
Patient acceptance of wearable devices goes beyond how well they function. Here are key factors that shape user adoption:
Device Aesthetics
- Design elements like size, weight, and visual appeal significantly impact patient willingness to wear devices consistently
- Sleek, minimalist designs often receive higher acceptance rates compared to bulky, medical-looking devices
- Color options and customizable features help patients feel more connected to their devices
Comfort Considerations
- Material selection affects skin sensitivity and long-term wearability
- Ergonomic design reduces physical discomfort during extended use
- Flexible attachment options accommodate different body types and user preferences
Integration with Daily Life
- Battery life optimization minimizes disruption to regular activities
- Water-resistant features allow normal hygiene routines
- Sleep-friendly designs ensure 24/7 data collection without compromising rest
User Interface Design
- Intuitive controls reduce learning curves and user frustration
- Clear feedback mechanisms help patients understand device status
- Simple data visualization increases engagement with health metrics
Cultural Sensitivity
- Design elements that respect cultural norms and preferences
- Gender-specific considerations in device placement and appearance
- Language support for diverse patient populations
Social Acceptance
- Discrete wearing options for different social situations
- Professional appearance for workplace environments
- Style variations that match different age groups’ preferences
Research shows that patients are more likely to maintain consistent device usage when wearables align with their personal style and lifestyle preferences. A study by the Digital Medicine Society found that 78% of participants ranked device aesthetics among their top three considerations for long-term use.
Design Implementation Strategies
To address these factors influencing patient acceptance, manufacturers can adopt the following strategies:
Early User Testing
- Prototype evaluation with diverse patient groups
- Feedback collection on design preferences
- Iterative refinement based on user input
Customization Options
- Interchangeable bands or covers
- Adjustable display settings
- Multiple wearing positions
Environmental Considerations
- Climate-appropriate materials
- Activity-specific durability
- Context-aware functionality
The intersection of medical functionality and consumer design principles creates wearables that patients want to use rather than feel obligated to wear. This shift in perspective transforms compliance from a challenge into a natural behavior pattern.
Successful implementation requires balancing regulatory requirements with user experience design. Manufacturers must maintain clinical-grade accuracy while creating devices that feel like personal accessories rather than medical instruments.
Strategies to Enhance User Experience Beyond Usability Testing
Creating a positive user experience with wearable devices in clinical trials extends far beyond basic functionality. Let’s explore proven strategies that drive participant engagement and satisfaction:
Personalization Features That Matter
- Custom alert settings aligned with individual daily routines
- Adjustable display options for visual comfort
- Flexible wearing positions to accommodate different body types
- Personalized progress tracking dashboards
- Language preferences and accessibility options
Gamification Elements for Enhanced Engagement
- Achievement badges for consistent device wear time
- Progress bars showing study milestone completion
- Virtual rewards for meeting data collection goals
- Social elements allowing anonymous peer comparisons
- Weekly challenges to maintain motivation
The success of these engagement strategies relies on continuous feedback loops:
- Regular participant surveys
- Focus group discussions
- Usage pattern analysis
- Real-time behavioral data collection
Design Considerations for Long-term Use
- Lightweight materials for comfort
- Fashion-forward aesthetics
- Battery life optimization
- Intuitive interface design
- Minimal maintenance requirements
Patient acceptance significantly impacts trial outcomes. Research shows that participants who find their wearable devices engaging and personally relevant are:
- 75% more likely to complete the full trial duration
- 60% more accurate in their data reporting
- 40% more likely to recommend trial participation to others
By implementing these user experience enhancements, research teams can create a more engaging and sustainable clinical trial environment that benefits both participants and researchers while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Integration of Digital Technologies into Clinical Trials
The integration of digital technologies into clinical trials represents a transformative shift in research methodology. Digital tools revolutionize traditional trial processes through:
Enhanced Data Collection
- Real-time physiological monitoring
- Automated vital sign recording
- Continuous activity tracking
- Sleep pattern analysis
A notable example of this is the enhanced data collection in a Phase III oncology study, where digital innovation and patient engagement significantly improved data quality and study outcomes.
Streamlined Recruitment
- Digital prescreening platforms
- Remote eligibility assessments
- AI-powered participant matching
- Virtual consent processes
Planning successful technology integration requires careful consideration of several key factors:
1. Technical Infrastructure
- Secure data transmission systems
- Cloud storage capabilities
- Backup protocols
- Integration with existing systems
2. Staff Training Requirements
- Device operation protocols
- Troubleshooting procedures
- Data interpretation guidelines
- Emergency response plans
Hybrid Study Designs: Combining Traditional Methods with Digital Tools
Hybrid study designs blend conventional clinical trial elements with digital innovations. This approach offers distinct advantages:
Remote Monitoring Benefits:
- Reduced site visits
- Decreased participant burden
- Improved compliance tracking
- Enhanced safety monitoring
These benefits are particularly relevant in the context of navigating wear compliance issues in remote healthcare monitoring where the use of wearables for remote monitoring has seen an exponential increase.
Physical Assessment Integration:
- Baseline measurements
- Complex diagnostic procedures
- Critical safety evaluations
- Face-to-face consultations
Real-World Success Stories:
The DETECT study demonstrated successful implementation of hybrid design by combining wearable heart rate monitoring with traditional cardiac assessments. This approach identified 85% more cardiac events compared to standard monitoring alone.
Implementation Strategies:
Phased Integration:
- Start with pilot programs
- Gradual technology adoption
- Regular assessment points
- Iterative improvements
Participant Support:
- Technical assistance hotlines
- Educational resources
- Regular check-ins
- Troubleshooting guides
Quality Assurance Measures:
- Data validation protocols
- Device calibration checks
- Signal quality monitoring
- Cross-verification procedures
The success of hybrid designs depends on:
- Clear communication channels
- Robust technical support
- Flexible protocol adaptation
- Strong participant engagement
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
Backup data collection methods:
- Manual data entry options for non-compliant participants
- Telephone interviews as an alternative to in-person assessments
Alternative monitoring plans:
- Switching to centralized monitoring in case of device failures
- Utilizing local healthcare providers for critical evaluations when necessary
These integrated approaches create a balanced research environment that maximizes data quality while maintaining participant comfort and study feasibility. The power of automated workflows in digital healthcare and connected devices further enhances this balance, providing new avenues for patient care and data collection as highlighted in our exploration of the power of automated workflows in digital healthcare.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Wearables play a significant role in clinical trials by providing real-time data on patient health and behavior, enhancing data collection methods, and facilitating remote monitoring. Their integration into trials can lead to improved patient engagement and more accurate outcomes.
The primary regulatory bodies overseeing wearable technology in clinical trials include the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States and the EMA (European Medicines Agency) in Europe. Each body has its own set of regulations that impact how wearables are utilized in research.
To ensure data quality throughout the trial process, it is essential to implement appropriate quality control measures at each stage of the data lifecycle. This includes careful monitoring during data collection, storage, and analysis phases to minimize errors and maintain reliability.
Compliance requirements for wearable technology in clinical trials include adherence to regulations such as 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records, GDPR for data protection in Europe, and HIPAA for patient privacy in the U.S. These regulations ensure validity and security throughout the trial process.
Ethical considerations include ensuring participant consent, addressing privacy concerns associated with continuous monitoring, and evaluating proposals through ethics committees to prioritize participant welfare alongside scientific advancement. Transparency and robust communication strategies are crucial for building trust.
Patient acceptance can be enhanced by focusing on user-friendly designs that cater to participants' preferences and incorporating personalization features based on feedback. Additionally, visual appeal plays a crucial role; thus, aesthetic considerations should not be overlooked when designing wearable devices.