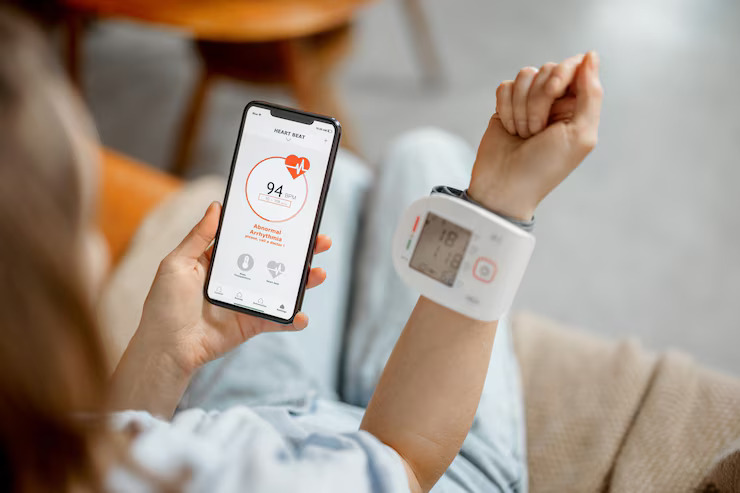
Wearable technology in healthcare is revolutionizing the way we monitor and manage our health. These devices, ranging from smartwatches to textile-based sensors, provide continuous health data that is invaluable for both patients and healthcare providers.
Definition of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
Wearable technology refers to electronic devices that can be worn on the body, often incorporating sensors and software to track various health metrics. Common examples include the Apple Watch, FitBit, and textile-integrated biosensors.
Importance of Tracking Health Data
Tracking health data through wearables offers significant benefits:
- Real-time monitoring: Enables immediate feedback on vital signs.
- Data-driven insights: Facilitates better decision-making for both patients and clinicians.
- Chronic condition management: Provides continuous oversight for conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Overview of the Blog’s Focus on Trends and Implications
This blog will explore the latest trends in wearable technology for healthcare, including:
- Integration of AI tools.
- Remote patient monitoring.
- Wearables embedded in textiles.
- Data management and security challenges.
In our previous article on how wearables are collecting data, we discussed how wearable devices like FitBit and Apple Watch have been widely adopted by consumers, providing valuable health data. The adoption of wearable technology has accelerated due to its potential in decentralized clinical trial design. However, one challenge remains – accessing and leveraging all this data effectively.
Furthermore, the integration of AI tools is another significant trend in wearable technology. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of health data collected from wearables, providing valuable insights for both patients and clinicians. This has the potential to revolutionize healthcare decision-making and treatment plans.
Remote patient monitoring is also gaining traction as wearables allow healthcare providers to monitor patient’s health remotely, reducing hospital visits and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the integration of wearables into textiles opens up new possibilities for unobtrusive health monitoring, creating more user-friendly devices.
As we explore these trends and their implications for healthcare delivery, it’s crucial to address challenges such as data management and security. The volume of data collected by wearables requires robust systems to ensure privacy and integrity throughout its lifecycle.
Wearable technology is transforming healthcare by providing real-time monitoring, data-driven insights, and improved chronic condition management. As we unravel the latest trends in this field, it’s essential to consider solutions like Clinical StudyPal that make wearable data accessible for clinical research purposes and the integration of AI tools to unlock the full potential of these devices in improving patient outcomes.
1. Disease Specific Algorithms
AI tools are essential for improving the accuracy and analysis of health data collected through wearable technology. These tools use machine learning algorithms to discover meaningful patterns and trends in the data that might otherwise be missed.
How AI Enhances Data Accuracy and Trend Analysis
- Data Filtering: AI can remove irrelevant or noisy data, ensuring that only useful and accurate information is examined.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models can forecast potential health problems by studying past data trends, enabling proactive healthcare.
- Personalized Insights: AI-powered wearables offer customized health advice based on each user’s specific data characteristics.
Examples of AI Applications in Healthcare Wearables
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Devices like the Apple Watch utilize AI to track heart rate and rhythm, notifying users of any irregularities.
- Glucose Monitoring: Wearables equipped with AI can continuously measure glucose levels, sending immediate alerts to diabetic patients.
- Sleep Tracking: Advanced AI algorithms analyze sleep patterns, providing information about sleep quality and suggesting ways to improve it.
These advancements not only benefit individuals in managing their health but also have significant potential for clinical research. Delve Health offers valuable insights into how wearables, devices, and data are transforming clinical trials.
For example, one area where the impact of integrating wearables is most evident is in remote patient monitoring. It allows healthcare providers to monitor patients outside of traditional healthcare settings, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced hospitalizations.
By using AI effectively, wearable technology in healthcare not only improves data accuracy but also provides actionable insights for better health outcomes.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring
Benefits for Patients with Chronic Conditions
Remote patient monitoring significantly enhances the quality of life for individuals managing chronic conditions. By enabling continuous health tracking, patients can detect anomalies early and seek timely medical intervention. This proactive approach not only improves health outcomes but also reduces hospital readmissions and emergency room visits.
Case Studies: How Remote Patient Monitoring is Revolutionizing Healthcare
A notable example is MultiCare’s use of the Apple Watch. This initiative monitors heart rate and rhythm notifications, supporting cardiac rehabilitation patients. The real-time data provided by wearables allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions without requiring patients to visit the clinic frequently.
MultiCare’s success illustrates:
- Enhanced patient engagement
- Improved adherence to treatment plans
- Reduced healthcare costs through preventive care
Real-Time Self-Monitoring Capabilities
Wearables offer unparalleled real-time self-monitoring capabilities. Devices like smartwatches and biosensors allow users to track vital signs such as:
- Heart rate
- Blood glucose levels
- Physical activity
This continuous data stream empowers patients with valuable insights into their health status, promoting better self-management of chronic conditions. Additionally, healthcare providers can leverage this data to tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
3. Wearables Embedded in Textiles for Home Healthcare
Innovations in textile-based wearables are revolutionizing home healthcare by seamlessly integrating health monitoring into everyday clothing. These cutting-edge solutions provide non-intrusive ways to track vital signs and other health metrics, offering continuous monitoring without disrupting daily activities.
Innovations in Textile-Based Wearables
Recent advancements include:
- Smart fabrics: These textiles can detect and transmit data on heart rate, temperature, and movement.
- E-textiles: Embedded sensors in clothing that monitor physiological data.
- Flexible electronics: Integrated circuits within fabrics that provide real-time health insights.
Advantages for Remote Care and Patient Comfort
Wearable technology embedded in clothing offers numerous benefits, particularly for remote care:
- Enhanced comfort: Patients feel more at ease wearing familiar clothing rather than bulky devices.
- Continuous monitoring: Real-time data collection helps healthcare providers keep track of patients’ conditions remotely.
- Improved compliance: Comfortable, non-intrusive wearables increase patient adherence to monitoring protocols.
These innovations support the growing demand for remote healthcare solutions, aiming to enhance patient outcomes and comfort.
4. Addressing Data Management and Security Challenges in Wearable Technology
Wearable technology in healthcare offers significant benefits, but it also brings along data management challenges and security concerns. As wearables collect vast amounts of health data, managing this influx efficiently becomes crucial.
Issues Related to Data Overload and Privacy Concerns
- Data Overload: Wearable devices continuously monitor various health metrics such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. This constant stream of data can lead to information overload, making it difficult for healthcare providers to extract actionable insights quickly.
- Privacy Concerns: The sensitive nature of health data collected by wearables raises serious privacy issues. Unauthorized access to this data can lead to misuse or breaches, compromising patient confidentiality.
Recommendations for Ensuring Secure Data Transmission
- Encryption: Implementing robust encryption protocols ensures that data transmitted from wearable devices to healthcare systems remains secure.
- Authentication Mechanisms: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) can add an extra layer of security, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive health information.
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic security audits helps identify potential vulnerabilities in the system, enabling timely interventions.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhering to standards such as HIPAA and GDPR ensures that data handling practices meet regulatory requirements, thereby enhancing trust.
The use of wearables for remote healthcare monitoring and clinical trials has been on the rise in recent years due to their numerous advantages. These devices hold untapped potential regarding their probable ability to revolutionize the manner in which we conduct clinical trials and remote monitoring, which will eventually also transform how medical treatment is delivered around the world.
For instance, leveraging the Apple Watch for seamless data collection has proven to be a groundbreaking approach in clinical research. The integration of wearables like the Apple Watch, FitBit, and other devices into clinical trials not only encourages healthy behavior but also offers a more efficient and accurate method of data collection. This could eventually lead to improved patient outcomes and enhanced research results, making wearables the future of clinical research.
Integrating Wearable Data with Clinical Systems: Challenges and Opportunities

Integrating wearable data with clinical systems presents a range of challenges that healthcare providers must navigate. This integration is crucial for creating a holistic patient health view, yet it’s fraught with complexities.
Integration Difficulties with Clinical Systems and APIs
- Data Compatibility: Wearable devices often generate data in varying formats, making it difficult to integrate seamlessly with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
- APIs and Interoperability: Many healthcare systems use proprietary APIs, which can limit the ability to share data across different platforms.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Clinical systems may struggle to process the continuous stream of data from wearables, requiring robust computing power and real-time analytics capabilities.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring secure data transmission and compliance with regulations like HIPAA is critical but challenging when integrating multiple systems.
Opportunities:
- Enhanced Patient Monitoring: Successful integration allows for continuous monitoring, providing clinicians with real-time insights into patient health.
- Improved Clinical Outcomes: Better data integration leads to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
For instance, platforms like Delve Health have demonstrated success in leveraging wearable technology for clinical trials, showcasing the potential benefits of seamless integration in studies related to conditions such as Parkinson’s disease.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from both technology providers and healthcare institutions. Solutions like standardized data formats and interoperable APIs are crucial steps toward effective integration. For detailed insights on digital data capture tools enhancing accuracy and engagement in clinical trials, explore this comprehensive guide on eCOA and ePRO.
Navigating these complexities can unlock significant advancements in patient care and clinical research, driving the future of healthcare technology forward.
Successful Implementations of Wearables in Clinical Trials
Overview of How Wearables are Used in Clinical Trials
Wearable devices in clinical trials offer a groundbreaking way to collect real-time data, track patient adherence, and enhance overall study efficiency. These devices provide continuous monitoring of physiological parameters such as:
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Glucose levels
- Physical activity
This continuous data collection helps researchers gain more accurate and comprehensive insights into patient health, thus improving the quality and reliability of clinical trials.
Case Study on Delve Health’s Clinical StudyPal Platform
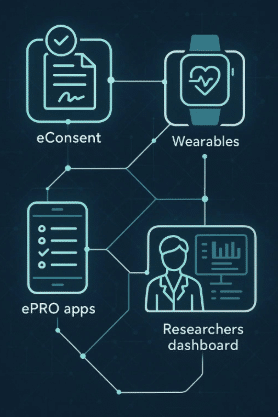
Delve Health’s Clinical StudyPal platform exemplifies the effective integration of wearable technology in clinical trials. This platform supports diverse populations by enabling remote health data collection and analysis at scale. Key features include:
- Real-time monitoring: Allows for immediate data capture and intervention.
- Patient engagement: Keeps participants involved and committed through user-friendly interfaces.
- Secure data transmission: Ensures compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and CFR Part 11 standards.
For instance, Delve Health recently partnered with Withings Health Solutions to revolutionize clinical trials at home. This collaboration aims to utilize Withings’ innovative wearable devices for remote virtual studies, making the trials more efficient and inclusive.
Additionally, the Apple Watch has emerged as a powerful tool in clinical trial settings. Its FDA-approved Class II status, combined with its sleek design and advanced functionality, enables it to conduct remote virtual trials effectively.
These implementations demonstrate how wearable technology can revolutionize clinical research by making it more efficient, inclusive, and precise.
Future Directions for Wearable Technology in Healthcare
Potential Advancements on the Horizon
Wearable technology is ready for significant advancements that promise to reshape healthcare delivery. Key areas of innovation include:
- Biosensors: These devices can monitor a variety of physiological parameters. They are increasingly being integrated into wearables, providing more accurate and comprehensive health data.
- Advanced AI Algorithms: Enhanced AI will improve the accuracy of health monitoring and predictive analytics, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Enhanced Data Interoperability: Improved integration with electronic health records (EHRs) will streamline data flow between patients and healthcare providers.
Strategies to Promote Adoption Among Underserved Populations
Ensuring equitable access to wearable technology is crucial. Strategies to promote adoption among underserved populations include:
- Subsidized Devices: Offering affordable or subsidized wearables can make them accessible to low-income individuals.
- Community-Based Programs: Initiatives that educate communities about the benefits of wearable tech can drive adoption.
- Focus on Maternity Care: Addressing inequity in maternity care through dedicated programs that provide wearables for monitoring maternal health.
Wearable technology holds the potential to bridge gaps in access to healthcare and clinical trials, ensuring more inclusive and effective health interventions. For example, Delve Health’s role in digital biomarkers explores how wearables and digital biomarkers are transforming patient outcomes by gathering data differently, enabling more realistic clinical research. Additionally, as wearables gain traction in the healthcare world at-large, it becomes crucial to focus on delivering devices and safely collecting real-world data (RWD) from them, as they are being implemented in more and more clinical trials. These devices enable a clinical study team to monitor their patients’ various health metrics, like daily steps, sleep quality, and heart rate, increasing patient compliance and retention. By incorporating these advancements and strategies, the future of wearable technology in healthcare looks promising, ensuring broader access and improved health outcomes for all populations.
Conclusion
Understanding the growth of wearable technology in healthcare highlights its transformative potential in enhancing patient care, monitoring, and overall health outcomes. By integrating advanced tools such as AI, remote monitoring systems, and textile-based wearables into clinical practice, we can achieve more accurate data collection and improved patient engagement.
Encouraging the adoption of these technologies is crucial. Leveraging the latest trends can lead to significant improvements in managing chronic conditions, ensuring secure data transmission, and providing real-time health insights.
Healthcare professionals and researchers are encouraged to explore platforms that enhance clinical trials through optimized workflows and wearable technology. Delve Health offers a comprehensive platform that significantly enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical trials. By leveraging their solution which integrates wearable technology with optimized patient workflows, we can achieve better results in our studies.
Furthermore, one important aspect to consider when conducting clinical trials is the device selection. To guide you through this process, Delve Health provides valuable insights on Consideration for Device Selection in Clinical Trials. This resource discusses key factors that should be taken into account when selecting a device for your study.
Embracing these trends will pave the way for a future where healthcare delivery is not only more efficient but also more personalized, leading to better health outcomes for all.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Wearable technology in healthcare refers to devices that can be worn on the body to monitor health metrics and track data, enhancing patient care and providing real-time insights into an individual’s health status.
AI enhances wearable technology by improving data accuracy and trend analysis. It helps identify meaningful data patterns, enabling better decision-making for patient care through applications such as predictive analytics and personalized health recommendations.
Remote patient monitoring offers significant benefits for patients with chronic conditions, including continuous health tracking, timely intervention opportunities, and enhanced communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to improved health outcomes.
Innovations in textile-based wearables include smart clothing that can monitor vital signs and other health metrics seamlessly. These advancements provide advantages for remote care by enhancing patient comfort while allowing continuous health monitoring.
Challenges related to data management in wearable technology include data overload and privacy concerns. Ensuring secure data transmission is crucial, and recommendations include implementing robust encryption methods and adhering to regulatory standards for data protection.
Future trends in wearable technology for healthcare may include advancements like biosensors that provide real-time health monitoring. Additionally, strategies will be developed to promote adoption among underserved populations, addressing inequities in access to healthcare services.