Wearable technology in healthcare refers to electronic devices that individuals can use to monitor various health metrics continuously. These devices, ranging from fitness trackers and smartwatches to more advanced medical devices like glucose monitors and ECG monitors, provide real-time data crucial for both preventive and chronic disease management.
This article explores:
The Evolution of Wearable Technology in Healthcare: Traces the historical development and significance of wearable devices.
Key Applications of Wearable Technology in Medicine: Examines the roles of continuous health monitoring, preventive healthcare, and patient empowerment.
Benefits and Challenges Ahead: Discusses the advantages and hurdles faced by wearable medical devices.
Enhancing User Experience in Wearable Technology: Highlights design considerations for optimal user experience.
The Future Landscape of Wearable Technology in Healthcare: Looks at emerging trends and the role of big data, AI, and collaborative platforms.
Dive into how these advancements are shaping the future of medical devices and revolutionizing patient care.
For more insights on how technology is transforming clinical trials, check out our article on how we design clinical trials with wearables, devices, and data which explores the challenges faced by clinical research teams during the pandemic.
Furthermore, if you’re interested in understanding the differences between “digital endpoints” and “patient outcomes” in clinical trials, you can also read our comprehensive piece on the subject – Digital Endpoints and Patient Outcomes in Clinical Trials: Understanding the Differences and Similarities.
The Evolution of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
Historical Development and Significance of Wearables in Healthcare
Wearable technology has come a long way from simple fitness trackers to sophisticated medical devices. Initially, these devices were primarily used by fitness enthusiasts to track physical activities such as steps taken and calories burned. Over time, the technology evolved to include smartwatches that could monitor heart rate, and sleep patterns, and even detect irregular heart rhythms. These advancements have made wearable health monitoring devices an integral part of personal healthcare management.
Transition to Advanced Medical Devices with Consumer Appeal
The shift towards integrating advanced medical functionalities into consumer-friendly devices is exemplified by innovations like Neuralink. This brain implant aims to merge consumer electronics with medical technology, offering potential benefits such as real-time brain activity monitoring and treatment for neurological conditions. Such advancements highlight the trend of developing medical devices that are not only functional but also appealing to consumers.
Challenges in Design and Ethical Implications
Merging consumer electronics with medical technology presents unique challenges in both design and ethics:
Design Challenges: Balancing functionality with user comfort and battery life is critical.
Ethical Implications: Ensuring data accuracy, patient information security, and regulatory compliance are paramount concerns.
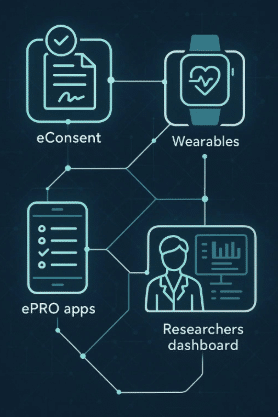
Addressing these challenges is essential for the successful integration of wearable technology in healthcare. For instance, eConsent in Virtual Clinical Trials plays a crucial role in ensuring informed consent through electronic systems and processes, which is particularly relevant given the FDA’s guidance on this matter.
Furthermore, wearable technology is revolutionizing clinical trials by enabling Delve Health’s Wearable-as-a-Service, which reduces costs and improves real-world evidence creation. This innovation opens up new possibilities for more efficient and impactful research outcomes.
Key Applications of Wearable Technology in Medicine
1. Continuous Health Monitoring
Continuous health monitoring is a game-changer for managing chronic diseases. Wearable devices like glucose monitors and wearable ECG monitors empower patients to track their health metrics in real time, providing critical data that can prompt timely medical interventions.
Examples of Continuous Health Monitoring Devices:
- Glucose Monitors: Devices such as the Dexcom G6 CGM System allow individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels continuously. This real-time monitoring helps in maintaining optimal glucose levels, reducing the risk of complications.
- Wearable ECG Monitors: Products like the Apple Watch Series with AFib detection and wearable ECG monitors provide continuous heart rate monitoring. This is crucial for detecting cardiac abnormalities early, which can prevent severe cardiac events.
The importance of continuous health tracking cannot be overstated. For chronic disease management, consistent monitoring enables:
- Timely Interventions: Immediate alerts on irregularities allow for faster medical response, potentially saving lives.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Continuous data collection helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment plans.
For an in-depth look at how digital healthcare and connected devices are transforming patient outcomes, visit The Power of Automated Workflows in Digital Healthcare & Connected Devices by Delve Health.
2. Preventive Healthcare
Wearables play a pivotal role in preventive healthcare by leveraging AI and predictive analytics. These technologies help in early disease detection, allowing for proactive management rather than reactive treatment.
How Wearables Contribute to Preventive Healthcare:
- Predictive Analytics in Wearables: Machine learning algorithms analyze the data collected by wearables to predict potential health issues before they become critical.
- Early Disease Detection: Devices equipped with predictive analytics can identify patterns indicating the onset of conditions such as cardiovascular diseases or diabetes.
This approach shifts the focus from treatment to prevention, significantly improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
3. Patient Empowerment
Wearable technology empowers patients by giving them an active role in their healthcare management. Real-time monitoring and personalized feedback facilitate better health outcomes through:
- Facilitating Data-Driven Decisions: Patients can make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment based on real-time data from their wearables.
- Active Role in Care: With continuous access to their health metrics, patients are more engaged and proactive in managing their health.
For insights into how wearables are transforming patient outcomes and the role of digital biomarkers in clinical research, explore Transforming Patient Outcomes: The Role of Wearables and Digital Biomarkers in Clinical Research provided by Delve Health.
Integrating continuous health monitoring with preventive healthcare strategies not only enhances individual well-being but also contributes to a more efficient healthcare system. Wearable technology stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering unprecedented opportunities for improving patient care and outcomes.
To learn more about incorporating wearable technology into clinical trials, including remote patient monitoring and considerations for device selection, visit Delve Health’s comprehensive resources on the subject.
2. Preventive Healthcare
Wearable technology plays a pivotal role in preventive healthcare, leveraging AI and Machine Learning (ML) to usher in a new era of early disease detection. By using predictive analytics in wearables, these devices can analyze continuous health monitoring data to predict potential health issues before they become severe.
How Wearable Technology Enables Preventive Healthcare
1. AI and ML
These technologies enable wearables like glucose monitors and wearable ECG monitors to detect anomalies in real time, providing immediate alerts to both patients and healthcare providers. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, potentially preventing serious health complications.
2. Predictive Analytics
Through sophisticated algorithms, wearables can identify patterns and trends that might indicate the onset of conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases. For example, a wearable ECG monitor can track heart rhythms continuously, alerting users to irregularities that could signify an upcoming cardiac event.
3. Patient Empowerment
Real-time monitoring empowers patients by giving them access to their health data, enabling them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options. This data-driven empowerment fosters a more engaged and proactive approach to personal health management.
Digital endpoints are also revolutionizing clinical trials through real-time monitoring. These digital endpoints have a positive effect on clinical trials by providing more accurate and comprehensive data for analysis, thereby enhancing the efficacy of medical research.
By integrating AI/ML capabilities into wearable devices, the healthcare industry can significantly enhance early disease detection and improve patient outcomes. These advancements represent a leap forward in the quest for predictive wearables that not only monitor health but also prevent diseases before they manifest.
Discover how closing the gap in patient care standards is crucial for achieving these goals. As clinical trials are a critical part of medical research, this link explains how we can overcome the challenges of recruiting patients and ensure their active participation in these studies.
3. Patient Empowerment
Wearable technology in healthcare is changing how patients interact with their health information, promoting patient empowerment through continuous health monitoring and immediate feedback.
Making Informed Choices with Data
Devices like wearable ECG monitors and glucose monitors give patients important information about their health numbers. This data helps individuals make smart decisions about their lifestyle and treatment choices. By using advanced analysis in wearables, patients can spot early warning signs and take action to manage long-term conditions effectively.
Patients Taking Charge of Their Own Health
Being able to monitor their vital signs in real time allows patients to keep track of their body functions all the time. This active involvement changes patients from being passive receivers of care to proactive managers of their own health. For example:
Remote patient monitoring systems allow the gathering of health data such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
Patients can then share this information with their healthcare providers for more informed discussions and personalized treatment plans.
The combination of wearable technology in healthcare systems is leading to a significant change towards preventive healthcare and data-based choices, giving patients the ability to manage their well-being better than ever before.
For instance, Delve Health’s article on Delivering Devices and Safely Collecting Real-World Data (RWD) explains how wearables are being used in more clinical trials, allowing a research team to monitor different health metrics while increasing patient compliance and retention. This opens up new possibilities for data collected by wearable devices.
To learn more about how wearable technology is making clinical trial data accessible, you can also read Delve Health’s insights on Wearables Collect Data—Clinical StudyPal Makes Data Accessible, which explores how wearables improve clinical research and support decentralized trial design.
Benefits and Challenges of Wearable Medical Devices
1. Continuous Monitoring and Timely Interventions
Wearable technology in healthcare provides continuous monitoring capabilities that are crucial for managing chronic diseases. Devices such as glucose monitors, ECG monitors, and smartwatches can track vital signs in real time, alerting both patients and healthcare providers to any irregularities. This immediate feedback enables timely interventions, potentially averting medical emergencies.
2. Impact on Patient Outcomes and Hospital Costs
Personalized healthcare solutions offered by wearables can significantly improve patient outcomes. For instance, continuous glucose monitors help diabetic patients maintain optimal blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications. Similarly, wearable ECG monitors can detect early signs of cardiac issues, allowing for prompt medical attention.
Reducing hospital visits and minimizing the need for extensive diagnostic tests also lowers healthcare costs. According to predictions, wearable devices could reduce hospital costs by up to 16% over the next five years.
Enhancing User Experience in Wearable Technology
Integrating Design with Functionality and Data Utilization
User experience in wearable tech depends on how well design, functionality, and data utilization work together. An intuitive design is crucial for ensuring that users can easily use their devices without needing a lot of training. Here are some important things to think about:
- Simplicity: Keep interfaces simple and prioritize the most important functions.
- Accessibility: Include features that can be used by different types of users, including those with disabilities.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Use physical feedback (like vibrations) and visual cues (like flashing lights) to give users real-time information.
Wearable devices should not only collect health data accurately but also present that data in a way that’s easy for users to understand. This includes having clear and simple displays on the device itself, as well as sending notifications to a connected smartphone app. The goal is to provide information that helps users make informed decisions about their health.
Importance of Integration with Apps/Cloud Storage for Seamless Usability
For wearables to work well, they need to be able to connect with other devices like smartphones and cloud storage services. This kind of integration is important because it allows:
- Real-Time Data Syncing: The ability to automatically update information between the wearable device and a smartphone or tablet.
- Remote Monitoring: Healthcare providers can keep track of patient’s health data even if they’re not in the same location, which could reduce the number of in-person appointments needed.
- Data Analytics: Using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to analyze large amounts of health data and identify patterns or trends.
Making sure that wearables can easily connect with apps and cloud storage often requires working with developers who specialize in these areas. Some companies offer platforms specifically designed for healthcare applications, such as Delve Health, which focuses on real-time data collection for outcome assessments.
Hardware Considerations for Comfort and Battery Life
The physical design of wearable devices also plays a big role in user experience. Two important factors to consider are:
- Ergonomics: Wearable devices should be lightweight and comfortable to wear for long periods of time.
- Battery Life: Having a battery that lasts a long time means users don’t have to charge the device as often, making it more convenient to use.
Using innovative materials and smart engineering techniques can help improve comfort without sacrificing durability. Similarly, choosing energy-efficient components can help extend battery life, which is a common concern among users.
It’s important for companies working on wearable technology to pay attention to these hardware considerations while also staying up-to-date with new trends and technologies. For example, Delve Health specializes in addressing compliance issues in remote healthcare monitoring, ensuring that their devices meet both regulatory standards and user expectations.
The future of wearable technology will likely involve even more integration between design, functionality, and data utilization. The goal is to create devices that seamlessly fit into people’s lives and help them manage their health more effectively.
The Future Landscape of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
1. Innovations on the Horizon
Wearable technology in healthcare is rapidly evolving, with several emerging trends that promise to revolutionize how we monitor and manage health.
Smart Health Clothing
Smart clothing integrates sensors into everyday garments to monitor various health metrics. These advanced textiles can measure physiological signals such as heart rate, respiration rate, and body temperature. For instance, smart shirts equipped with ECG sensors provide continuous heart monitoring, which can be crucial for patients with cardiac conditions.
Brain Implants for Continuous Monitoring
Implants like Neuralink are pushing the boundaries of wearable tech by enabling direct brain-computer interfaces. These implants have the potential to monitor neurological activity continuously, offering new insights into brain health and aiding in the management of neurological disorders. This technology could pave the way for advanced treatment options for conditions such as epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
Predictive Wearables
Predictive wearables leverage AI and machine learning algorithms to foresee potential health issues before they become critical. Devices that predict seizures or detect irregular heart rhythms illustrate this capability, enabling timely medical interventions and improving patient outcomes.
Big data in healthcare plays a pivotal role here. By analyzing vast amounts of data collected from these wearables, healthcare providers can identify patterns and make more informed decisions. The integration of AI in healthcare is projected to grow significantly, with market predictions estimating it could reach $148 billion by 2029.
Delve Health explores how “wearables” are changing clinical research by offering virtually limitless possibilities in terms of data collection and patient engagement.
Wearable Devices in Clinical Trials
Wearables are transforming clinical trials by offering real-time data collection and monitoring capabilities. Platforms like Delve Health utilize wearable devices to improve patient engagement and streamline trial processes. This approach not only enhances data accuracy but also reduces the burden on participants by minimizing the need for frequent site visits.
Collaborative Platforms
Platforms like Delve Health provide seamless integration with existing clinical trial systems, enabling secure data transmission while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as HIPAA and GDPR. These platforms harness big data analytics to offer actionable insights from wearable device data, supporting groundbreaking medical research.
The integration of eClinical trials is set to become the new standard for conducting clinical research. They significantly reduce the patient burden while increasing patient recruitment and retention, as well as boosting study staff’s efficiency via automated workflows—saving time and cutting operational costs. However, there are growing concerns regarding data privacy when conducting virtual clinical studies, as well as the potential challenges that are created for sponsors to maintain HIPPA and/or GDPR compliance.
2. The Role of Big Data, AI, and Collaborative Platforms
The development of wearable technology is heavily influenced by big data and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies make it possible to analyze large amounts of health data collected by wearables, leading to significant advancements in healthcare.
How Big Data and AI Are Making a Difference
- Big Data in Healthcare: Collects patient information from different sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of health patterns and trends.
- AI in Healthcare Market Predictions: The market is expected to grow to $148 billion by 2029, showing its increasing impact.
- Predictive Wearables: Use AI algorithms to predict potential health problems before they become serious, enhancing preventive care.
Using Wearables for Gathering Data in Clinical Trials
- Wearable Devices in Clinical Trials: Enable continuous monitoring and real-time data collection, reducing the need for frequent visits to the research site.
- Delve Health’s Platform: Supports diverse and underrepresented populations by offering access to quality healthcare and clinical trials through wearable technology. Their platform ensures secure data transmission and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
By combining smart clothing, and implants such as Neuralink, and utilizing big data, AI, and collaborative platforms, wearable technology will continue to revolutionize the healthcare industry.
Conclusion
Wearable technology is set to transform the healthcare landscape significantly. The integration of advanced sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI capabilities in wearable devices is offering unprecedented opportunities for continuous health monitoring, preventive care, and personalized treatment plans.
The Promising Future of Wearable Technology in Revolutionizing Healthcare
Here are some ways wearable technology can benefit healthcare:
- Continuous Health Monitoring: Devices such as smartwatches and ECG monitors provide real-time insights into vital signs, enabling the early detection of potential health issues.
- Preventive Care: Predictive analytics powered by AI can forecast health risks before they become serious conditions, allowing for timely interventions.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Wearables can track individual health metrics over time, facilitating tailored healthcare solutions that cater to unique patient needs.
Encouragement for Continued Innovation and Investment
Investment in wearable technology is crucial for driving future advancements. Innovators and investors should focus on:
- Enhancing Data Accuracy: Improving sensor technology to ensure precise and reliable health data.
- Ensuring Security: Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information.
- Improving Accessibility: Making wearables affordable and accessible to a broader population.
Stakeholders must collaborate to overcome existing challenges and unlock the full potential of wearables in healthcare. This concerted effort will pave the way for innovative solutions that can revolutionize patient care and improve overall health outcomes
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Wearable technology in healthcare refers to electronic devices that can be worn on the body, often equipped with sensors that monitor health metrics. These devices enable continuous health monitoring, and real-time data collection, and facilitate preventive healthcare measures.
Key applications of wearable technology in medicine include continuous health monitoring for chronic disease management, preventive healthcare through predictive analytics, and enhancing patient empowerment by enabling data-driven decisions and remote patient monitoring.
Wearable medical devices provide numerous benefits such as personalized healthcare solutions, continuous monitoring for timely interventions, improved patient outcomes, and potential reductions in hospital costs. They also empower patients to take an active role in their own care.
Challenges facing wearable technology in healthcare include concerns over data accuracy and reliability, ensuring patient information security and regulatory compliance (such as HIPAA), and addressing issues related to accessibility and affordability for widespread adoption.
Enhancing user experience in wearable technology involves integrating intuitive design with functionality, ensuring seamless usability through integration with apps and cloud storage, and considering hardware aspects such as comfort and battery life to improve overall user satisfaction.
The future landscape of wearable technology in healthcare includes innovations like smart clothing and brain implants (e.g., Neuralink), advancements driven by big data and AI, and the utilization of wearables in clinical trials. Continuous innovation and investment are crucial for realizing the full potential of these technologies.